Deploy Airflow to GKE from ArgoCD on GKE with Workload Identity
How to deploy an Argo CD service on GKE autopilot, and setup an Airflow application to deploy on another GKE cluster using workload…
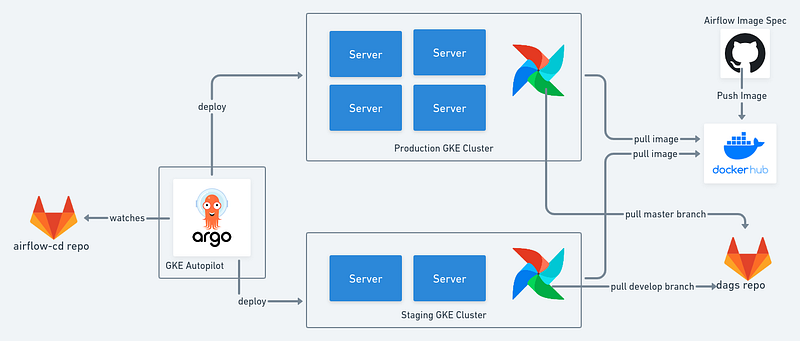
In the previous post I explained how to build and host one’s own Airflow image, that would be the top right corner of this architectural diagram.
In another post I also explained a bit about deploying Airflow with Argo CD from official helm chart and use customize to tailor for different environments.
This post aim to run through the whole process again but now entirely on GKE. Having been managing our own airflow for a while, the time for solving hardware and network related issues (not to mention storage class issues) is eating up our devops team resource, and we decide that it is worth the cost to migrate the entire airflow deployment on GKE.
If you decide to use GKE’s Composer, you may skip this tutorial completely, as Composer manages Airflow for you. We decide to host our own Airflow to have more granular control over resources and deployment strategy. This is our architectural setup:
- Deploy Airflow on GKE Autopilot.
- Setup GKE Standard cluster for Airflow deployment.
- Setup Workload Identity so that service accounts in Argo CD can impersonate a service account to operate on Google’s Kubernetes API.
- Create Argo CD application with proper cluster configuration, and set the destination to external cluster.
Refer to https://github.com/schwannden/argocd-operator and https://github.com/schwannden/airflow-operator to get started, the remaining article is a step by step walk through and explanation.
Deploying Argo CD to GKE Autopilot
Here are the things we need to do to be able to deploy Argo CD on GKE
https://github.com/schwannden/argocd-operator/tree/main/base
- disable ssl in
argocd-server.yamlas we are deploying on to GKE, which means we are setting up ingress and load balancer service on GKE, therefore handling certificate on GKE load balancer. - disable https port in
service.yaml, same reason as above.
https://github.com/schwannden/argocd-operator/tree/main/overlays/gke
in overlays/gke, we configure google load balancer (frontend, backend, and ingress) in ingress.yaml.
Enable Workload Identity
The steps to enable workload identity are outlined here (codes are in repo):
Variable Definitions (reference: https://github.com/schwannden/argocd-operator/blob/main/workload-identity/.env)
GSA_PROJECT: the project to create google service account that would grant GKE access, this should be the project hosting your GKE that host the Argo CD application.GSA_NAME: the name of the service account that will be grating permission to deploy application to target cluster.GKE_PROJECT: the project where you want to allow the Kubernetes service account to impersonate the IAM service account, i.e., the project where you create your GKE cluster and enable is workload identity.NAMESPACE: argocd’s namespaceTARGET_PROJECT: the project hosting the destination GKE cluster of your Argo CD application.
Steps in detail:
- Enable GKE’s workload identity
Enable workload identity for the GKE that deploys Argo CD, refer to official document. - Create a Google service account
gcloud iam service-accounts create ${GSA_NAME} — project=${GSA_PROJECT}- Grant the Google service account permission to operate on target GKE
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding ${TARGET_PROJECT} \
--member=serviceAccount:${GSA_NAME}@${GSA_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--role=roles/container.developer- Grant the argocd kubernetes service accounts to act as google service account
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding ${GSA_NAME}@${GSA_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--role roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser \
--member "serviceAccount:${GKE_PROJECT}.svc.id.goog[${NAMESPACE}/argocd-application-controller]"
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding ${GSA_NAME}@${GSA_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--role roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser \
--member "serviceAccount:${GKE_PROJECT}.svc.id.goog[${NAMESPACE}/argocd-server]"- Annotate the Kubernetes service account with the email address of the IAM service account
kubectl annotate serviceaccount argocd-application-controller --namespace argocd \
iam.gke.io/gcp-service-account=${GSA_NAME}@${GSA_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.com
kubectl annotate serviceaccount argocd-server --namespace argocd \
iam.gke.io/gcp-service-account=${GSA_NAME}@${GSA_PROJECT}.iam.gserviceaccount.comNow you are all set! Your Argo CD can now use workload identity, and the 2 service accounts (argocd-server and argocd-application-controller) now have permission to do so.
Creating Argo CD Application
With the following application spec you may point destination to your target GKE cluster
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: airflow
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: 'your-airflow-operator-url'
path: overlays/production
plugin:
name: kustomized-helm
destination:
namespace: airflow
server: https://your-gke-endpoint
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: false
selfHeal: false
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=trueAnd you may supply cluster certificcate to Argo CD as follows
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: ndpoint-airflow-cluster-secret
namespace: argocd
labels:
argocd.argoproj.io/secret-type: cluster
type: Opaque
stringData:
name: your-cluster-endpoint
server: your-cluster-endpoint
config: |
{
"execProviderConfig": {
"command": "argocd-k8s-auth",
"args": ["gcp"],
"apiVersion": "client.authentication.k8s.io/v1beta1"
},
"tlsClientConfig": {
"insecure": false,
"caData": "your-cluster-certificate-in-base64"
}
}Congratulations! You should be able to host your own Airflow!
And let us not grow weary of doing good, for in due season we will reap, if we do not give up.
Happy Hacking!